The “Five Forces” that Porter identified are: Rivalry Customers Suppliers Buyers Competition He suggested that companies focus on the bargaining power of their customers, suppliers and competitors, and the new company’s relative bargaining power will become the focus of the newly established company.
Porter’s five forces is a framework for understanding the competitive environment in which a product or company operates. The framework breaks down competition into five business subcategories: 1. Threat of New Entry. 2. Bargaining Power. 3. Threat of Substitutes. 4. Bargaining Power of Suppliers. 5. Threat of New Entry.
In order to analyze a particular industry using porter’s five forces, we first need to determine the industry. Let’s use the automobile industry as the example. We can logically look at the following five forces that shape the industry. (In this example we will be analyzing the industry using the automotive industry.
However, if you would like to analyze another industry, feel free to use what you have.) 1. The threat of New Entrants: The threat of new entrant is high since every other company is trying to enter the industry. Competition is very high since every other company is trying to enter the industry. There are many companies in the industry and most of them are trying to enter the industry. 2. Threat of Substitutes
A company operating in a competitive industry (sector) cannot demonstrate a competitive advantage. But a company living in a monopoly (like Microsoft) has an exclusive advantage. So an industry with too many competitors is not good for their business. As buyers, we want to buy products from companies that operate in the competitive space. But as investors, we would love to buy shares in a company with a monopoly. It is easier to find a monopoly firm if you first define an area where such competition does not exist. How do you do that? With the five rules proposed by Michael Porter, professor at Harvard Business School. They are called Porter’s five forces. But before we discuss Porter’s five strengths, we need to understand what he means by competitive advantage.
What is a competitive advantage?

This is a profitable position that the company deserves. It is a position from which a company can operate with an advantage over its competitors. How does the company get a position? By building an economic moat for you. What’s the advantage? These companies have profitability well above their cost of capital. A business that can offer its customers something unique has the first advantage. But it is also true that the offering must be scalable (revenue growth). The combination of scalability and uniqueness gives the company a competitive advantage. Uniqueness does not have to be the driving force to gain an advantageous position.
It is more important to keep competition to a minimum. An example of this type of company is Coca-Cola and Pepsi. Their offering (soft drinks) is not that unique, but they have minimized the competition. How do you do that? Acquisition of competing brands worldwide.
Porter’s five forces for exploring competitive advantage
Pro-investors keep an eye on their company and others in the industry. But it may not be enough to follow the actions of all companies. For this reason, Michael Porter proposed a five-point scale in which the industry is ranked according to the degree of competition. The tougher the competition, the less likely a company is to have a competitive advantage.
The five parameters required by Porter’s rule are:
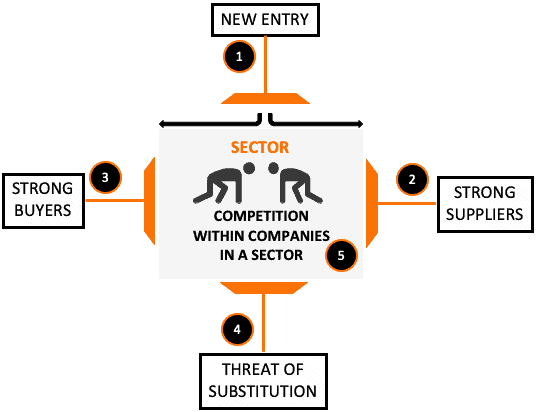
How difficult is it to join a sector/industrial sector
In some sectors/businesses, it is easy for new companies to enter and do business. This is good for promising companies, but not for existing companies (and their investors) in these sectors. They could lose market share and profits to new entrants. An industry that makes it harder for new firms to enter gives existing firms a competitive advantage in a sense. An investor wants to buy shares in companies operating in such a sector.
What could make it difficult for new businesses to enter the market?
- High capital requirements : Capital-intensive companies are less likely to have a new entrant trying its luck in that sector/industry. Think of an integrated steel plant like Tata Steel, JSW, JSPL, etc. Due to the high cost of setting up an integrated steel plant, fewer people are entering this sector.
- A strong brand identity: Customers buy certain products just because they look at the brand name. This one is viable in the medium luxury class. Few players have been in this business for many years. BMW and Mercedes are the two dominant companies. People who can afford a BMW aren’t going anywhere else.
- Low cost: Tata Steel has been a low-cost steel producer in India for decades. What makes them so profitable? Location of their factories, wealth of expertise, size, distribution network, etc. It will be almost impossible for a new steel producer to produce steel at the cost of Tata Steel.
- Large Volumes : Suppose a company wants to enter the FMCG sector manufacturing biscuits. The new entrant will compete not only with the big brands (such as Britannia and ITC), but also in terms of volume. To be competitive, a company must produce in large quantities. As a result, their products will be found on the shelves of all retail outlets alongside those of their main competitors. But producing in these quantities is a big challenge.
- State restrictions: Some sectors require state permits to do business. For example, not everyone is licensed in industries such as aviation, telecommunications, alcohol, multi-brand retail, banking, insurance, etc.
What is the influence of industry/suppliers?
Strong suppliers have more bargaining power. These suppliers can raise prices at will, resulting in lower profitability for the company. Investors want to buy shares of companies whose suppliers are not as influential. How can the strength of suppliers in the sector/industry be assessed?
- Few suppliers: Suppose there are only a few suppliers of products or services in an industry. These suppliers will have greater bargaining power. The company will have less control over its prices and the quality of its supplies.
- A unique product: The company buys a lot of goods from outside. In terms of cost, some purchases will be critical. Now suppose that the purchase is made from a supplier of a single product. For example, mobile phone manufacturers buy processors from Qualcomm. The suppliers of these excellent products are influential.
- Industry dependence : Some suppliers only supply a specific sector. These suppliers have minimal control over their customers. As investors, we want to buy shares of companies whose main suppliers are exclusively related to this sector.
What is the influence of buyers in the sector/industry?
Customers (clients) can also influence the competitive advantage of a sector/industry. If buyers have too much bargaining power, the industry will be forced to operate at low margins. Why? In fact, the buyer will push the company for low prices. How can the purchasing power of the sector/industry be estimated?
- Bunch of coppers: Suppose that only a few customers buy the products of the whole industry in large quantities. What kind of control do you think these buyers will have over the company? These companies will have a minimal competitive advantage.
- Easy change: Buying power is also enhanced when a company’s offerings are not unique. The customer does not have to pay to switch from one product to another. To retain these customers, the company will sell the goods at reduced prices.
- Price-sensitive buyers: If most buyers in an industry are too price sensitive, this will affect suppliers. Price sensitivity occurs when the buyer’s margins are low. These buyers buy goods at heavily discounted prices.
- Non-critical point: If the product sold is not essential to the customers, they will care less about its quality. When there is less emphasis on quality, people buy at an undervalued price.
The above four factors give buyers too much power. When an industry or sector is dominated by buyers, its firms have a low return on capital (ROC). As an investor, this is a clear sign of a weak competitive advantage.
Substitution risk
We have already discussed this in the above thread on purchasing power. But the threat of substitution looms, even if the buyers are not very influential. For example, an individual has virtually no purchasing power relative to a corporation. But the behavior of a collection of individuals can become problematic. How do you do that? If a company’s product is not unique, these people can easily change their choice. These companies have little pricing power. They can’t make their products too expensive. The product will also need to be marketed intensively to create a niche for itself. The combination of a low selling price and high marketing costs will reduce the profitability of the business.
Fierce competition from other companies
Although this question is in fifth place, it is the strongest. If too many firms are active in the same sector/industry, none of them can gain an advantage (competitive advantage). This becomes even more problematic when the quality of the products of these competing companies is the same. Therefore, to make ends meet, companies give deep discounts. These companies will also have to spend more on distribution and marketing of their products. This is why good companies are constantly developing new and unique products.
Supplement
It is very important for an investor to know the competitive advantages of the sector/industry. It is also important to be aware of the economic loophole of the sole proprietorship. For us as individual investors, it is difficult to identify the right companies for long-term investment. If we follow the tips below, we can better structure our search for quality companies:
- Industry study : Based on Porter’s five forces, as described above, we can first look at the industry/sector as a whole. The goal should be to identify the sector that is inherently less competitive. Good companies in these sectors will operate at a higher level of profitability.
- Business Research : Individually, we would like to invest in a bar steel company for the long term. It is a gap that gives the company pricing power. These companies have an above average return on capital.
- Value Search : It is critical for investors to buy stocks at undervalued prices. A promotion is only as good as the evaluation criteria used in its selection.
Competitive Advantage is the ability to create a product or service that is so superior that it can command a price premium over the competition. We are unable to create such products because we cannot keep up with the fast pace of technological change – we are behind the times, our products and services are not innovative, and we are not in a position to leverage our knowledge.. Read more about porter’s five forces and let us know what you think.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of Porters Five Forces?
Porter’s Five Forces focus on identifying threats, opportunities, and barriers in the market. Knowing these factors is quite helpful in understanding the competitive advantage of any company.
Thus, this analysis is used in the fundamental analysis of a company from a competition point of view.
How do you analyze an industry using Porter’s five forces?
There are many different models for industry analysis. Companies often rely on the five forces model to analyze industry forces that are important to their businesses.
These forces are defined as the industry structure, industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and competitive intensity.
What is Porter’s analysis?
Porter’s five forces is a model that shows how five key drivers of profitability in a specific industry can be used to understand the attractiveness of an industry. It’s a tool used by managers and investors to determine how competitive the industry is.
What are Porter’s five forces of competitive position analysis?
Porter’s Five Forces is an integrative framework to analyze the competitive forces at work in a business environment. It determines the intensity of competition in the market and the overall resilience of the business. A Porter’s Five Forces analysis evaluates the five key forces that determine the competitive position of a firm, and is an essential tool for industry leaders, managers, and strategic planners. Porter’s five forces of competitive position analysis is one of the most popular frameworks for studying a company’s competitive position. In particular, it is used to analyze the bargaining power of customers, suppliers, substitutes, competitors, and potential entrants in order to gauge a company’s position in an industry.
